Daemon Application in Linux or Service Application in Windows is an application that running in the background, usually automatically started when the operating system started even if user is not logged in. In Windows Service Application you cannot access Windows GUI library.
To create Daemon with Lazarus, first you need to create new project and select Daemon (service) application. After you click the OK button the IDE will create a new lazarus project with a daemon mapper unit dan a daemon class unit. Then save the project to the specified project name and folder.
Then you need to give the daemon class name. In this example the daemon class is named FirebirdRelayDaemon and the unit file saved as uFirebirdRelayDaemon.pas.The daemon class will never be registered to the operating system or started unless you register it in the Daemon Mapper. To register the daemon class you need to open the daemonmapperunit1.pas.
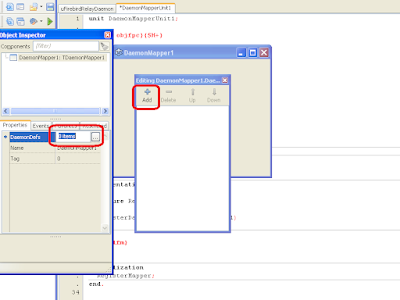
Then click the object inspector and then click the ellipsis button in the DaemonDefs property to open the daemon definitions editor. Then click Add button in the daemon definitions editor to add new daemon definition.
After you click Add button the object inspector will display the new daemon definition. You need to edit DaemonClassName, Display and Name properties.
- DaemonClassName: TFirebirdRelayDaemon.
- DisplayName: Firebird Relay Server.
- Name: firebirdrelayd.
After the daemon class is registered, you can place the code for your daemon in the daemon class. You can place objects initialization in the OnCreate event and objects finalization in the OnDestroy event. The code to start the daemon thread is placed in the OnStart event and code to terminate daemon thread is placed in the OnStop event.
This is the example of the daemon class declaration:
- type
- { TFirebirdRelayDaemon }
- TFirebirdRelayDaemon = class(TDaemon)
- procedure DataModuleCreate(Sender: TObject);
- procedure DataModuleDestroy(Sender: TObject);
- procedure DataModuleStart(Sender: TCustomDaemon; var OK: Boolean);
- procedure DataModuleStop(Sender: TCustomDaemon; var OK: Boolean);
- private
- { private declarations }
- FirebirdRelayServer: TFirebirdRelayServer;
- public
- { public declarations }
- end;
This is the example of the daemon class definition:
- { TFirebirdRelayDaemon }
- procedure TFirebirdRelayDaemon.DataModuleCreate(Sender: TObject);
- begin
- FirebirdRelayServer := TFirebirdRelayServer.Create;
- end;
- procedure TFirebirdRelayDaemon.DataModuleDestroy(Sender: TObject);
- begin
- FirebirdRelayServer.Free;
- end;
- procedure TFirebirdRelayDaemon.DataModuleStart(Sender: TCustomDaemon;
- var OK: Boolean);
- begin
- FirebirdRelayServer.LoadFromIniFile(ExtractFilePath(ParamStr(0))+'konfig.ini',
- 'FirebirdRelayServer');
- FirebirdRelayServer.StartThread;
- OK := True;
- end;
- procedure TFirebirdRelayDaemon.DataModuleStop(Sender: TCustomDaemon;
- var OK: Boolean);
- begin
- FirebirdRelayServer.TerminateThread;
- OK := True;
- end;
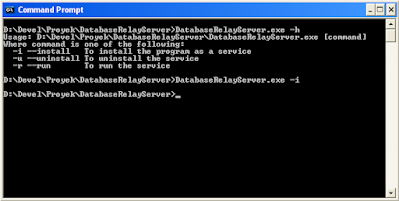
Output of the compiled daemon:
The daemon is installed in the windows services list:
You can start the service from command line using "net start firebirdrelayd" and stop the service using "net stop firebirdrelayd".
Thankyou for reading this article and I hope this article can be useful.









Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar